Understanding Modern Display Technologies: OLED, AMOLED, P-OLED, and LCD
At Interelectronix, we know the importance of choosing the right display technology for your products. Whether you’re considering OLED, AMOLED, P-OLED, Tandem OLED or LCD, this guide will help you understand the strengths and weaknesses of each, so you can make informed decisions that best suit your needs.
What is OLED?
OLED, or Organic Light Emitting Diode, uses organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. Unlike LCDs, OLEDs don’t require a backlight, allowing for true blacks and vibrant colors. OLED displays consist of several layers: a substrate (glass or plastic), an anode, organic layers, and a cathode. When electricity flows through these layers, each pixel lights up independently, offering high contrast ratios and energy efficiency.
OLED screens provide superior color accuracy and contrast. They’re thin and flexible, making them ideal for innovative designs like curved and foldable displays. They also offer excellent viewing angles and fast response times. However, OLEDs are more expensive to produce than LCDs, can suffer from burn-in with static images, and their organic materials can degrade over time, reducing lifespan.
What is AMOLED?
AMOLED, or Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode, is a type of OLED that uses an active matrix to control individual pixels. This technology, championed by Samsung, incorporates thin-film transistor (TFT) arrays to improve display efficiency and performance.
AMOLEDs are more power-efficient, especially with darker images, because only active pixels are powered. They offer higher refresh rates, making them ideal for gaming and video playback, and enhance brightness and color accuracy for a vivid viewing experience. Despite these advantages, AMOLEDs are costly to produce, can suffer from burn-in, and their manufacturing process is complex and expensive.
Samsung has led the way in AMOLED technology with its Super AMOLED displays, known for integrating the touch-sensor layer directly into the screen. This results in thinner displays with better touch sensitivity and reduced glare in sunlight, setting a high standard in mobile device display quality.
What is P-OLED?
P-OLED, or Plastic Organic Light Emitting Diode, is a variant of OLED that uses a plastic substrate instead of glass, enhancing flexibility and durability. This makes P-OLED displays suitable for a range of innovative applications.
P-OLED screens are flexible and lightweight, capable of withstanding more physical stress without breaking. They’re ideal for devices that need to be durable and portable. However, P-OLEDs are more expensive to produce due to advanced materials and manufacturing processes, and like other OLEDs, they can suffer from material degradation over time.
LG's Innovations with P-OLED
LG has been a significant proponent of P-OLED technology, leveraging its unique properties to create innovative products across various categories. LG has integrated P-OLED technology into several of its smartphones, such as the LG G Flex series. These devices featured curved screens that demonstrated the potential of flexible displays in enhancing user experience and design aesthetics. P-OLED is particularly well-suited for wearable devices like smartwatches, where flexibility and durability are crucial. LG has utilized P-OLED in its wearable devices to provide comfortable and resilient screens that can withstand daily wear and tear. LG has also explored the use of P-OLED technology in automotive displays. The flexibility and lightweight nature of P-OLED screens make them ideal for car dashboards and other in-vehicle displays, providing clear and vibrant visuals while adapting to the contours of the vehicle interior. LG has showcased various concept devices using P-OLED technology, including rollable and foldable displays. These concepts highlight the potential of P-OLED to revolutionize product design, offering new levels of versatility and user interaction.
Comparing OLED, AMOLED, P-OLED, and LCD
While OLED, AMOLED, and P-OLED are all based on the same fundamental technology, they each have unique characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. OLED displays are known for their superior color accuracy, high contrast ratios, and the ability to produce deep blacks. They are thin and flexible, offer wide viewing angles, and have fast response times. However, they can be expensive to produce and may suffer from burn-in and shorter lifespans due to organic material degradation. AMOLED builds upon OLED technology by incorporating active matrix control, which improves power efficiency, refresh rates, and overall display performance. These displays are particularly suited for mobile devices and applications requiring high-quality visuals and fast response times. Despite their benefits, AMOLED displays are also costly to produce and can suffer from burn-in. P-OLED stands out for its flexibility and durability, thanks to its plastic substrate. These displays are ideal for innovative form factors, such as curved, foldable, and rollable devices. While offering the benefits of OLED technology, P-OLED displays can be more expensive to produce and may face issues related to material degradation over time.
Comparing TFT LCD
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technology, while older, remains prevalent and offers several advantages. LCDs use a backlight to illuminate pixels, which are manipulated by liquid crystals to display images. This technology is less expensive to produce than OLED, AMOLED, and P-OLED, making it a cost-effective option for many applications. LCDs are also free from burn-in issues and have longer lifespans compared to OLED-based technologies. However, they generally offer lower contrast ratios and color accuracy because the backlight can’t be turned off at the pixel level, leading to less deep blacks and more muted colors. Despite these limitations, LCD technology continues to be widely used in a variety of devices, from televisions and industrial monitors to smartphones and tablets, due to its affordability and reliability.
The Future of Display Technology
The future of display technology promises exciting advancements. Foldable and rollable displays, enabled by the flexibility of P-OLED and AMOLED technologies, offer new levels of versatility. Enhanced durability is a key focus, with ongoing research aimed at improving the lifespan and reliability of OLED-based displays. Higher resolutions and refresh rates are becoming more critical, particularly for gaming, virtual reality, and professional content creation. Energy efficiency remains a priority, with innovations in AMOLED and P-OLED expected to yield more energy-efficient screens. Integration with other emerging technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and the Internet of Things (IoT), is also expected to drive new applications and use cases, such as embedding flexible OLED displays into smart clothing or home automation systems.
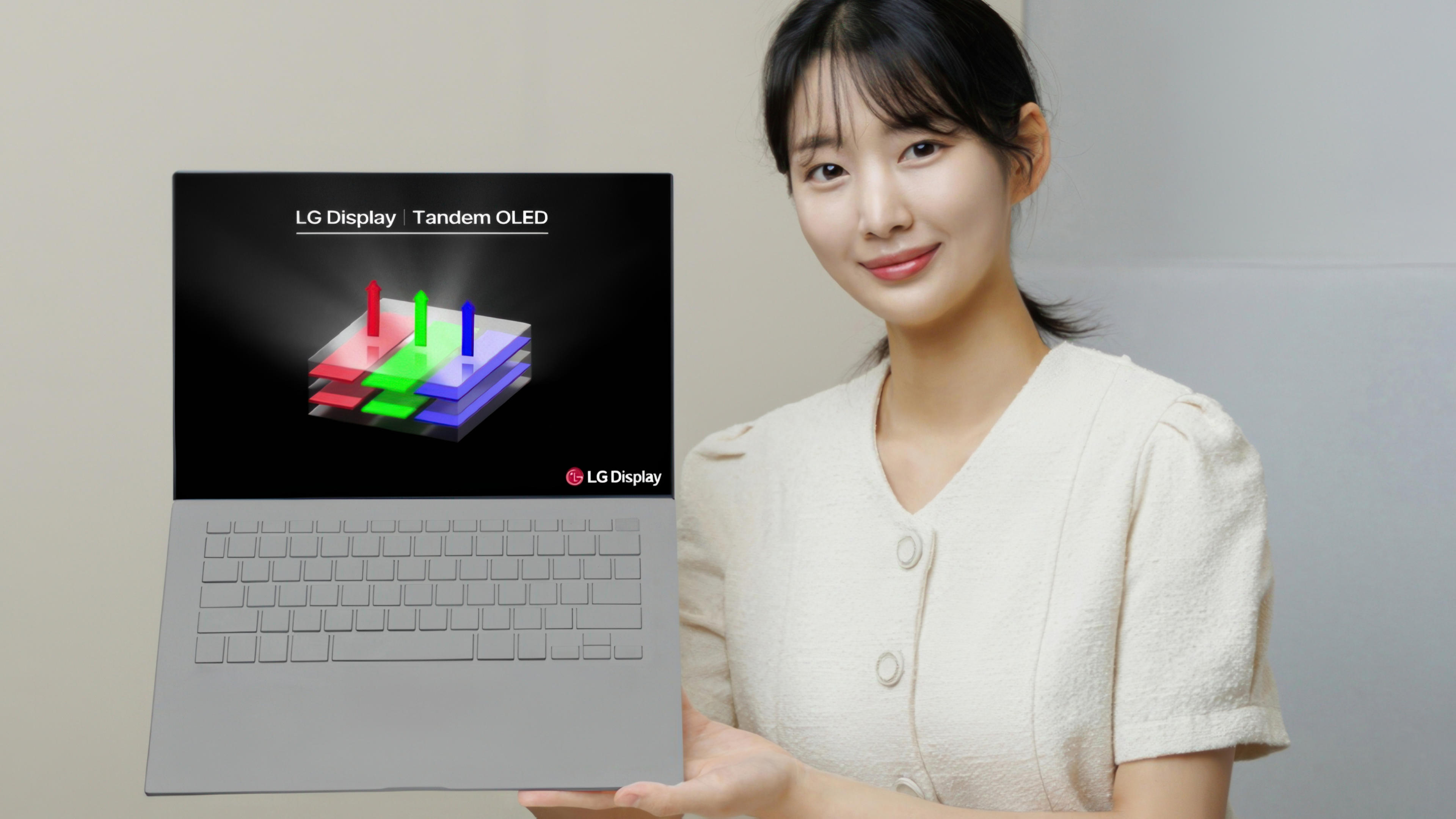
Tandem OLED
Discover the future of display technology with Tandem OLED panels, offering unmatched brightness, efficiency, and durability. Ideal for IT products, these advanced screens promise a new era of performance with up to 40% reduced power consumption and double the lifespan. Explore the benefits and transformative potential of Tandem OLED for superior quality displays.